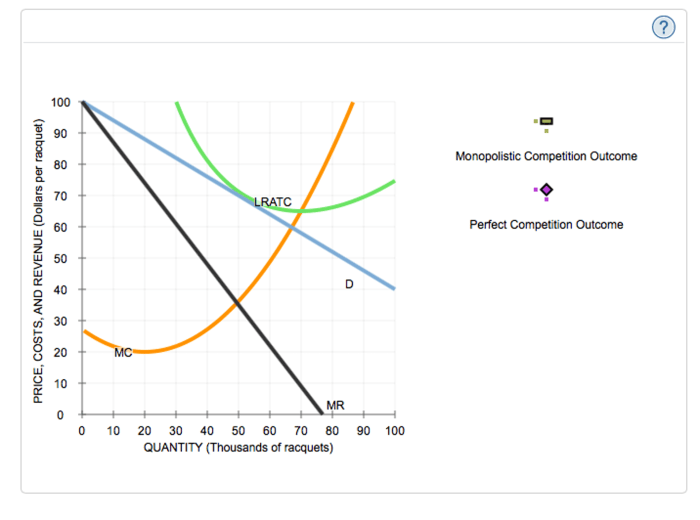
The graph below shows the monopolistically competitive market for smartphones. – The graph below shows the monopolistically competitive market for smartphones, a fascinating example of imperfect competition where numerous producers offer differentiated products within a single industry. This market structure, characterized by elements of both monopoly and perfect competition, presents unique insights into firm behavior, consumer preferences, and market efficiency.
In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the intricacies of monopolistic competition, examining its defining characteristics, supply and demand dynamics, producer and consumer behavior, and implications for market efficiency. By exploring real-world examples and utilizing economic theory, we aim to provide a thorough understanding of this prevalent market structure and its impact on the smartphone industry.
Market Structure
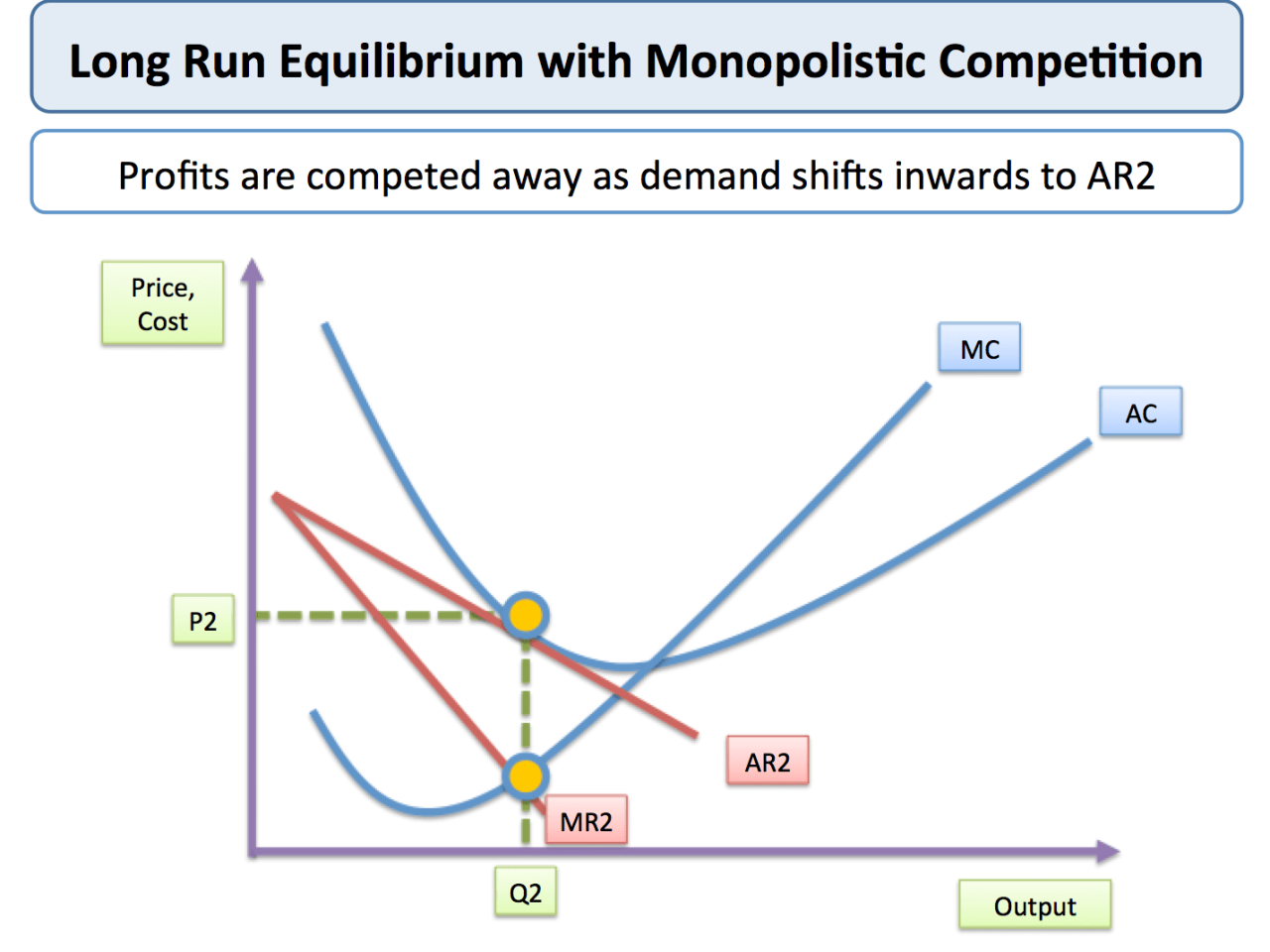
A monopolistically competitive market is a market structure characterized by many sellers offering similar but differentiated products. Each firm has a small market share and faces competition from numerous other firms. Product differentiation is a key feature of this market structure, as it allows firms to create unique products that appeal to specific consumer preferences.
Examples of real-world industries that exhibit monopolistic competition include the smartphone industry, the restaurant industry, and the clothing industry.
Product Differentiation
Product differentiation is a crucial element of monopolistic competition. By differentiating their products, firms can create a niche market for themselves and reduce the intensity of competition. Product differentiation can be achieved through various factors such as brand image, design, features, quality, and customer service.
Supply and Demand
| Quantity | Price | Supply | Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | P1 | S1 | D1 |
| Q2 | P2 | S2 | D2 |
| Q3 | P3 | S3 | D3 |
In a monopolistically competitive market, the equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves. At this point, the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, and there is no excess supply or demand.
Changes in demand or supply can impact the market equilibrium. An increase in demand will shift the demand curve to the right, leading to a higher equilibrium price and quantity. Conversely, a decrease in demand will shift the demand curve to the left, resulting in a lower equilibrium price and quantity.
Producer Behavior
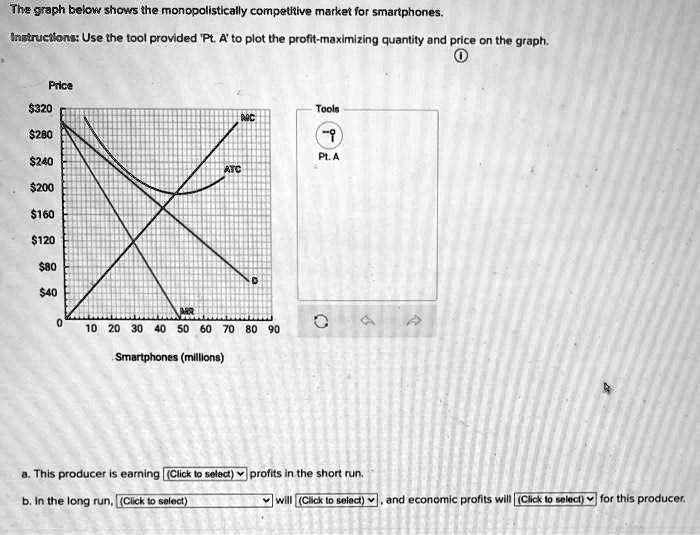
Firms in a monopolistically competitive market seek to maximize their profits. They use product differentiation to gain market share and create a loyal customer base. Firms may also engage in advertising and marketing to promote their products and influence consumer preferences.
Pricing and Output Decisions, The graph below shows the monopolistically competitive market for smartphones.
- Firms consider their marginal cost and marginal revenue when setting prices.
- Firms will produce output at the level where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
- Firms may also consider non-price factors such as brand image and customer loyalty when making pricing and output decisions.
Consumer Behavior: The Graph Below Shows The Monopolistically Competitive Market For Smartphones.
Consumer preferences play a significant role in shaping the demand for smartphones. Consumers consider factors such as price, features, brand, and design when making purchasing decisions.
Advertising and marketing can influence consumer choices by creating awareness, building brand loyalty, and highlighting product benefits. Consumers’ willingness to pay affects the market equilibrium, as it determines the maximum price that consumers are willing to pay for a product.
Market Efficiency
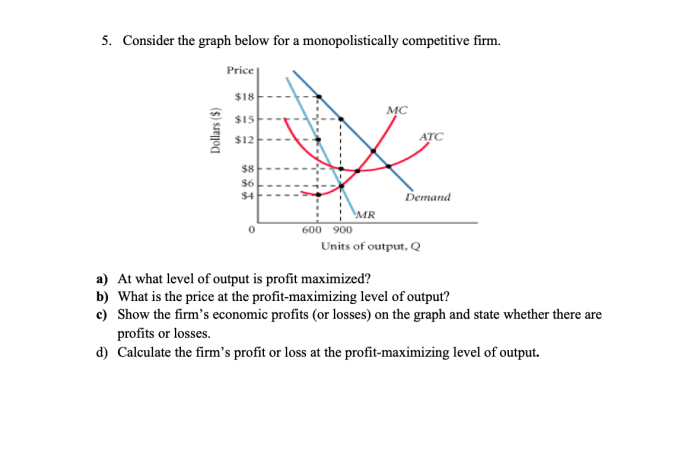
A monopolistically competitive market is generally considered to be more efficient than a monopoly but less efficient than perfect competition. It offers consumers a variety of choices and encourages innovation. However, product differentiation can lead to higher prices compared to perfect competition.
Potential market failures in monopolistic competition include:
- Inefficiently high prices due to product differentiation.
- Barriers to entry for new firms.
- Excess capacity due to firms producing differentiated products.
Detailed FAQs
What are the key characteristics of a monopolistically competitive market?
Monopolistic competition is characterized by numerous sellers offering differentiated products, easy market entry and exit, and interdependence among firms.
How is the equilibrium price and quantity determined in a monopolistically competitive market?
The equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the intersection of the market demand curve and the aggregate supply curve, which represents the horizontal summation of individual firm supply curves.
How does product differentiation impact firm behavior in a monopolistically competitive market?
Product differentiation allows firms to gain market power and charge a price above marginal cost, leading to higher profits compared to perfect competition.