Financial recommendations for clients answer key – Discover the intricacies of financial recommendations for clients, a critical aspect of financial planning. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights into understanding client needs, assessing risk tolerance, exploring investment options, and implementing effective financial strategies. By delving into this topic, financial advisors can enhance their ability to provide tailored recommendations that align with client goals and aspirations.
Financial recommendations for clients answer key serves as a roadmap for navigating the complexities of financial planning, empowering advisors to make informed decisions and achieve optimal outcomes for their clients.
1. Client Needs and Risk Tolerance

Understanding client’s financial goals and risk tolerance is crucial for making appropriate financial recommendations. Assessing client’s needs involves gathering information about their income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and future financial objectives. Risk tolerance, on the other hand, refers to the level of investment risk a client is willing and able to take.
It is influenced by factors such as age, investment horizon, and financial situation.
Assessing and Documenting Client’s Needs and Risk Tolerance
To assess client’s needs and risk tolerance, financial advisors use a variety of tools and techniques, including questionnaires, interviews, and financial planning software. The information gathered is then documented in a client profile, which serves as the foundation for developing financial recommendations.
Financial Products and Strategies for Different Risk Profiles
Based on client’s needs and risk tolerance, financial advisors recommend a range of financial products and strategies. For example, clients with a low risk tolerance may be advised to invest in conservative investments such as bonds or money market accounts, while clients with a higher risk tolerance may be advised to invest in growth-oriented investments such as stocks or mutual funds.
2. Investment Options and Recommendations
There are a wide range of investment options available, each with its own unique characteristics and risk-return profile. Common investment options include:
Types of Investment Options
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer potential for growth and income.
- Bonds: Loans made to companies or governments that pay interest and return the principal at maturity.
- Mutual Funds: Baskets of stocks or bonds that offer diversification and professional management.
- ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds): Similar to mutual funds, but traded on stock exchanges like stocks.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Investments, Financial recommendations for clients answer key
When selecting investments, financial advisors consider factors such as:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors to reduce risk.
- Growth Potential: The potential for an investment to increase in value over time.
- Risk: The potential for an investment to lose value.
Specific Investment Recommendations
Based on client’s needs and risk tolerance, financial advisors make specific investment recommendations. These recommendations may include:
- Asset Allocation: The distribution of investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash.
- Investment Products: Specific stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or ETFs that meet the client’s investment objectives.
- Investment Strategies: Long-term investment strategies such as value investing or growth investing.
3. Financial Planning Strategies
Financial planning involves developing a comprehensive plan to achieve long-term financial security. It encompasses a wide range of strategies, including:
Retirement Planning
Retirement planning focuses on saving and investing for a secure retirement. Strategies include maximizing retirement contributions, optimizing tax-advantaged accounts, and planning for income sources in retirement.
Tax Planning
Tax planning involves minimizing tax liability while maximizing after-tax income. Strategies include utilizing tax deductions and credits, optimizing investment strategies, and planning for estate taxes.
Estate Planning
Estate planning ensures the orderly distribution of assets after death. Strategies include creating a will or trust, planning for probate avoidance, and minimizing estate taxes.
Examples of Financial Planning Strategies
- Investing in a 401(k) plan with employer matching to maximize retirement savings.
- Utilizing a Roth IRA to save for retirement tax-free.
- Creating a living trust to avoid probate and ensure asset distribution according to wishes.
4. Risk Management and Monitoring
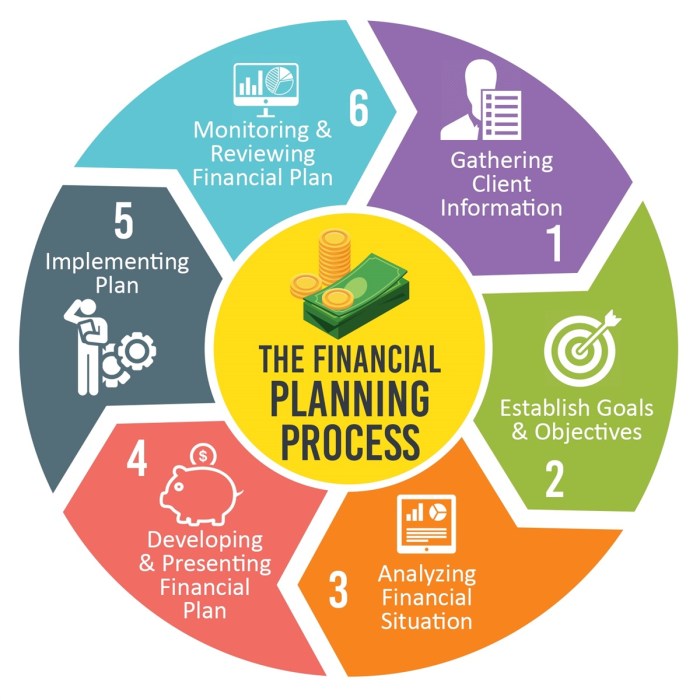
Risk management is an integral part of financial planning. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to financial well-being.
Risk Management Strategies
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors to reduce risk.
- Asset Allocation: Adjusting the distribution of investments based on risk tolerance and investment objectives.
- Hedging: Using financial instruments to offset the risk of adverse price movements.
Importance of Monitoring Investments
Monitoring investments is crucial to ensure that they are performing as expected and that the overall financial plan remains on track. Regular monitoring allows for timely adjustments to the investment portfolio as needed.
5. Communication and Reporting

Clear and effective communication is essential in financial planning. Financial advisors use a variety of methods to communicate financial recommendations to clients, including:
Communication Methods
- Written Reports: Detailed reports that provide a comprehensive overview of the client’s financial situation and recommendations.
- Presentations: In-person or virtual presentations that provide a visual representation of financial recommendations.
- Webinars: Online seminars that provide information and updates on financial topics.
Tips for Presenting Financial Information
- Use clear and concise language.
- Avoid technical jargon and use analogies or examples to simplify complex concepts.
- Tailor the communication to the client’s level of financial knowledge.
Q&A: Financial Recommendations For Clients Answer Key
What is the primary objective of financial recommendations for clients?
The primary objective is to provide tailored financial advice that aligns with individual client needs, goals, and risk tolerance, empowering them to make informed decisions and achieve their financial aspirations.
How can financial advisors assess client needs and risk tolerance?
Through comprehensive consultations, advisors gather information about client financial goals, time horizon, income, expenses, and risk tolerance. This assessment helps determine appropriate investment strategies and recommendations.
What factors should be considered when selecting investments for clients?
Factors to consider include diversification, growth potential, risk tolerance, investment horizon, and tax implications. Advisors evaluate these factors to create a portfolio that aligns with client objectives.