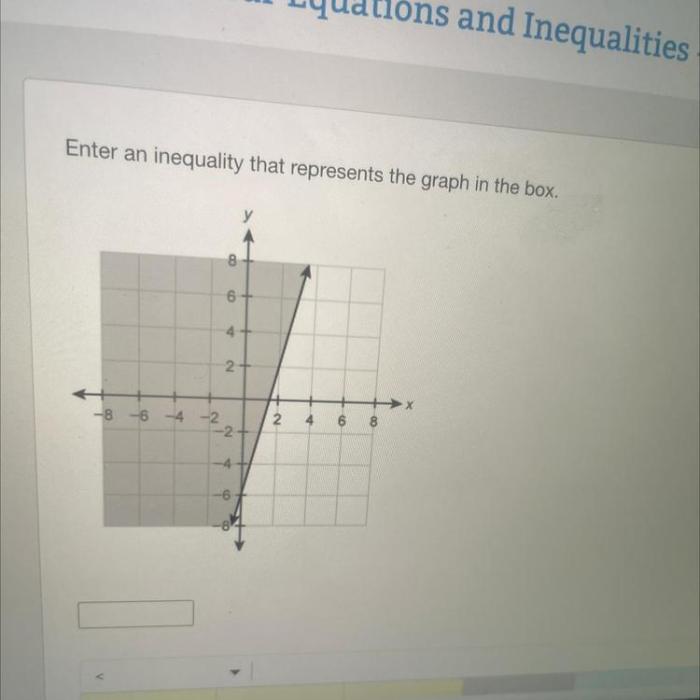
Enter an inequality that represents the graph in the box, a topic that invites us to delve into the realm of mathematics, where we explore the fascinating interplay between graphs and inequalities. This journey promises to illuminate the process of transforming a visual representation into a precise mathematical expression, empowering us to describe and analyze geometric shapes with newfound clarity.
As we embark on this exploration, we will uncover the secrets of boundary lines, shading regions, and slope-intercept forms, equipping ourselves with the tools to navigate the intricate world of linear inequalities. Prepare to witness the beauty of mathematics as we translate graphs into equations, unlocking a deeper understanding of geometric relationships.
Enter an Inequality that Represents the Graph in the Box
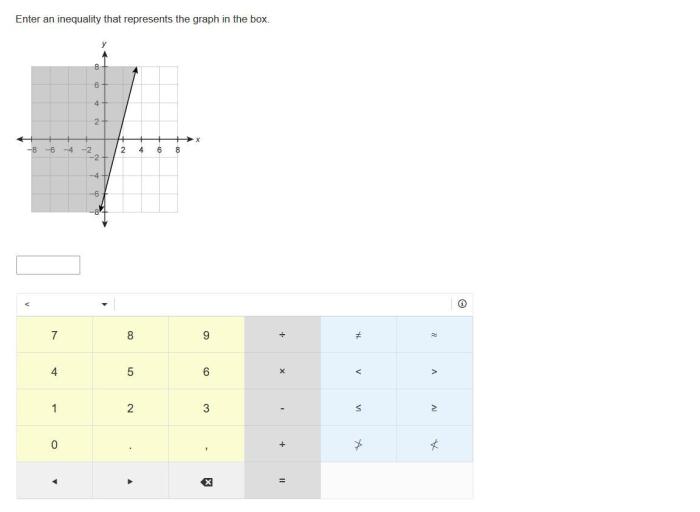
To represent a graph with an inequality, follow these steps:
- Identify the boundary line of the graph.
- Determine the slope and y-intercept of the boundary line.
- Write the inequality in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b).
For example, to represent the graph of the line y = 2x + 1, the inequality would be y ≥ 2x + 1.
Identify the Boundary Line of the Inequality, Enter an inequality that represents the graph in the box
The boundary line of an inequality is the line that separates the two regions of the graph: the region that satisfies the inequality and the region that does not.
To identify the boundary line, look for the line that is drawn with a solid line or a dashed line. The solid line indicates that the boundary line is included in the solution, while the dashed line indicates that it is not.
Determine the Shading Region of the Inequality
The shading region of an inequality is the region of the graph that satisfies the inequality.
To determine the shading region, look at the side of the boundary line where the shading is. If the shading is on the left side of the boundary line, then the inequality is satisfied when y is less than the boundary line.
If the shading is on the right side of the boundary line, then the inequality is satisfied when y is greater than the boundary line.
Write the Inequality in Slope-Intercept Form
Slope-intercept form is a way of writing an inequality in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope of the boundary line and b is the y-intercept.
To write an inequality in slope-intercept form, first find the slope and y-intercept of the boundary line. Then, substitute these values into the equation y = mx + b.
User Queries
How do I determine the boundary line of an inequality?
The boundary line is the line that separates the shaded region from the unshaded region. It can be determined by finding the equation of the line that passes through the points on the graph where the inequality changes from true to false or vice versa.
What is the shading region of an inequality?
The shading region is the area of the graph that satisfies the inequality. It is the region that is either above or below the boundary line, depending on the inequality.
How do I write an inequality in slope-intercept form?
To write an inequality in slope-intercept form, first solve the inequality for y. Then, write the equation in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.