The diffusion and osmosis problems answer key provides an invaluable resource for understanding the fundamental principles of diffusion and osmosis, their practical applications, and their implications in various fields. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of these key concepts, delving into their significance in everyday life and the factors that influence their rates.
From the intricacies of diffusion in biological systems to the industrial applications of osmosis, this guide unravels the complexities of these processes, providing a clear and concise explanation of their mechanisms and effects.
Diffusion and Osmosis: Key Concepts
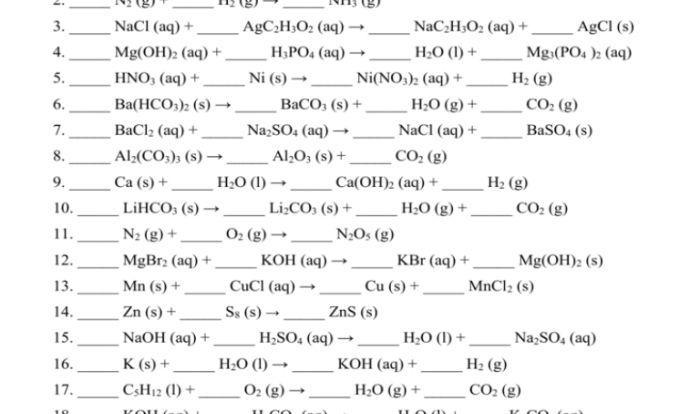
Diffusion and osmosis are fundamental processes that govern the movement of molecules and water across semipermeable membranes. Diffusion involves the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, driven by the random motion of molecules.
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that refers to the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
These processes play crucial roles in various biological and physical systems, including the transport of nutrients and waste in living organisms, the exchange of gases in lungs, and the purification of water in industrial settings.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Diffusion and Osmosis
- Concentration gradient:The greater the concentration difference between the two sides of the membrane, the faster the rate of diffusion or osmosis.
- Temperature:Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to faster diffusion and osmosis.
- Surface area of the membrane:A larger surface area allows for more molecules to pass through, increasing the rate of diffusion or osmosis.
- Thickness of the membrane:A thicker membrane provides more resistance to the movement of molecules, slowing down diffusion and osmosis.
Diffusion Problems
Practical Applications of Diffusion
- Gas exchange in lungs:Oxygen diffuses from the lungs into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide diffuses out.
- Nutrient absorption in the digestive system:Nutrients from food diffuse into the bloodstream through the walls of the intestines.
- Fragrance dispersion:Molecules of perfume or essential oils diffuse into the air, creating a pleasant scent.
- Drug delivery:Transdermal patches deliver drugs through the skin by diffusion.
Flowchart of the Diffusion Process, Diffusion and osmosis problems answer key
- Molecules are randomly distributed in an area.
- Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
- The movement of molecules continues until equilibrium is reached (i.e., the concentration becomes uniform throughout the area).
Osmosis Problems
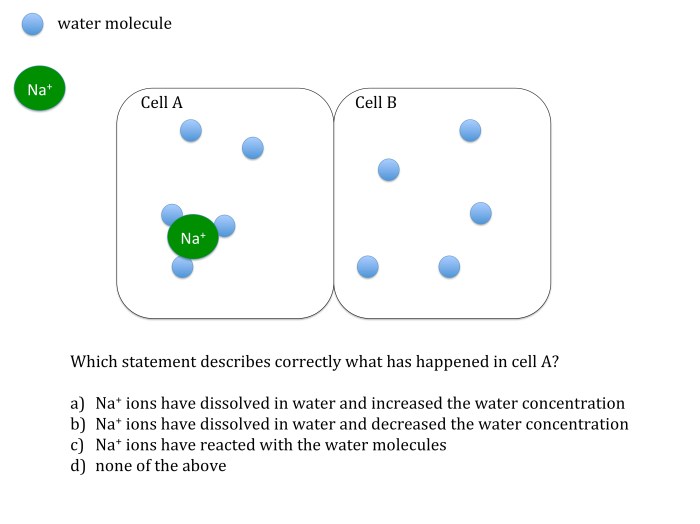
Role of Osmosis in Maintaining Water Balance
Osmosis is crucial for maintaining water balance in living organisms. Cells have a semipermeable membrane that allows water molecules to pass through while restricting the movement of most solutes. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution (lower solute concentration outside the cell), water moves into the cell by osmosis, causing it to swell.
Conversely, in a hypertonic solution (higher solute concentration outside the cell), water moves out of the cell, causing it to shrink.
Effects of Solute Concentration on Red Blood Cells
| Solute Concentration | Effect on Red Blood Cells |
|---|---|
| Hypotonic (lower outside) | Swell and burst (hemolysis) |
| Isotonic (equal inside and outside) | Maintain their normal shape |
| Hypertonic (higher outside) | Shrink and become crenated |
Applications and Implications: Diffusion And Osmosis Problems Answer Key
Medical Applications of Osmosis
- Dialysis:Removes waste products from the blood of patients with kidney failure by using a semipermeable membrane to allow toxins to diffuse out while retaining blood cells.
- Intravenous fluids:Administered to patients to restore fluid balance and electrolyte levels. The type of fluid used depends on the patient’s hydration status and electrolyte needs.
Industrial Uses of Osmosis
- Desalination:Converts saltwater into freshwater by using semipermeable membranes to remove salt ions.
- Food preservation:Osmotic dehydration removes water from food, inhibiting microbial growth and extending shelf life.
Environmental Implications of Osmosis
Changes in salinity due to osmosis can affect marine life. For example, sudden changes in salinity can cause osmotic stress in marine organisms, leading to physiological disturbances and even death.
Common Queries
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis?
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
What are the factors that affect the rate of diffusion?
The rate of diffusion is affected by temperature, concentration gradient, surface area, and membrane thickness.
What are the practical applications of osmosis?
Osmosis has a wide range of practical applications, including desalination, food preservation, and medical treatments such as dialysis.