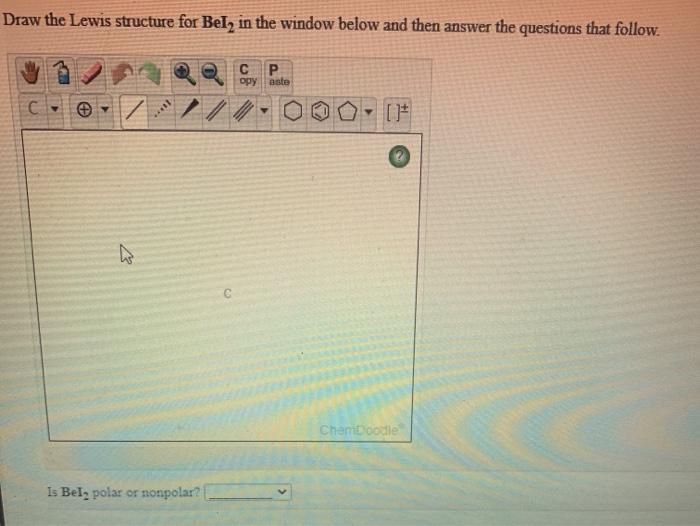
Is Bei2 polar or nonpolar? This intriguing question sets the stage for a captivating exploration into the realm of molecular polarity. Prepare to unravel the secrets of Bei2’s enigmatic nature as we delve into its fascinating properties and unravel the mysteries that surround its polarity.
Polarity, a fundamental concept in chemistry, plays a pivotal role in determining the behavior and interactions of molecules. Understanding the polarity of Bei2 opens a window into its unique characteristics, influencing its solubility, reactivity, and countless applications.
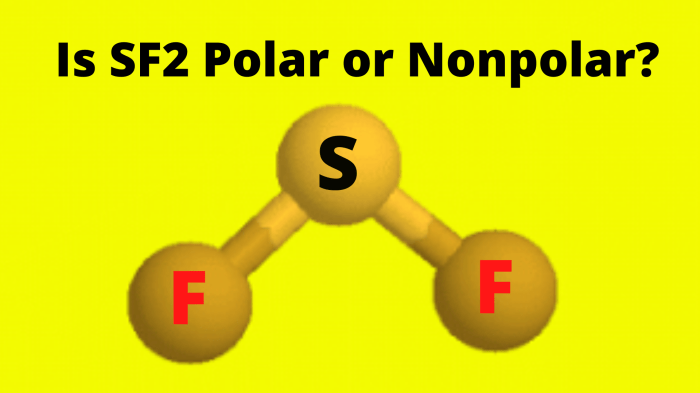
Polarity of Bei2
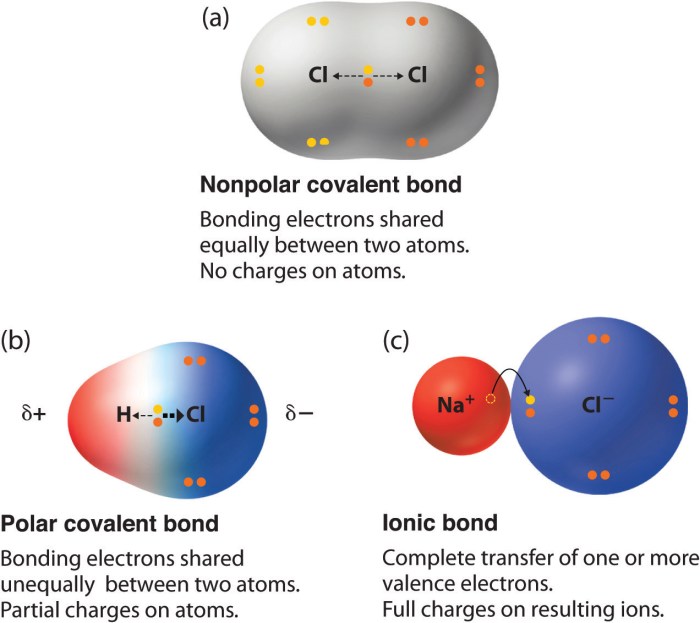
In chemistry, polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrical charge within a molecule. This uneven distribution creates a separation of positive and negative charges, resulting in a polar molecule. The polarity of a molecule is determined by the electronegativity of its constituent atoms, which is a measure of their ability to attract electrons.
There are two main types of polarity: permanent and induced. Permanent polarity occurs when there is a permanent separation of charge within a molecule, even in the absence of an external electric field. Induced polarity, on the other hand, occurs when a molecule is subjected to an external electric field, which causes the electrons within the molecule to shift, creating a temporary separation of charge.
Determining the Polarity of Bei2
Bei2 is a nonpolar molecule. This is because the two beryllium atoms in Bei2 have the same electronegativity, meaning that they have an equal ability to attract electrons. As a result, the electrons in Bei2 are evenly distributed between the two beryllium atoms, creating no separation of charge and thus no polarity.
Factors Influencing Polarity of Bei2
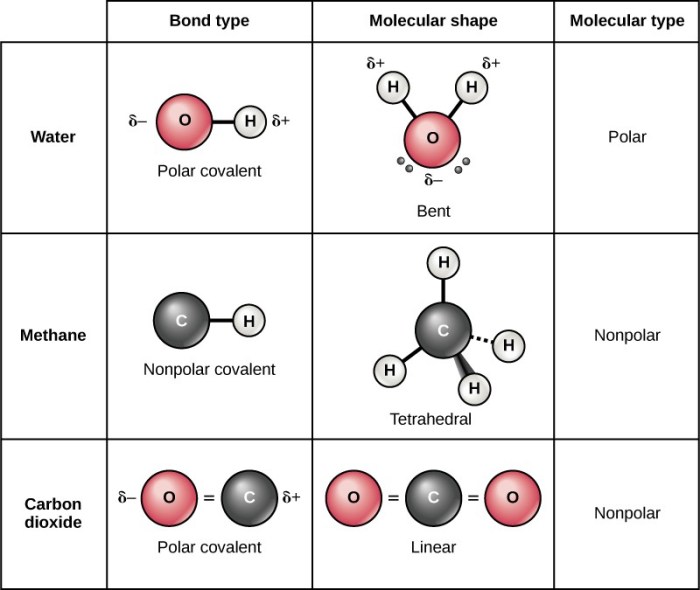
The polarity of Bei2 is determined by several factors, including electronegativity and molecular geometry.
Electronegativity, Is bei2 polar or nonpolar
Electronegativity refers to the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. In a bond between two different atoms, the more electronegative atom will attract the shared electrons more strongly, creating a polar bond. In the case of Bei2, the electronegativity of beryllium (Be) is 1.57, while that of iodine (I) is 2.66. This difference in electronegativity leads to a polar bond, with the iodine atom having a partial negative charge and the beryllium atom having a partial positive charge.
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry also plays a role in determining the polarity of a molecule. A molecule with a symmetrical geometry, such as a linear or tetrahedral molecule, will have no net polarity. However, a molecule with an asymmetrical geometry, such as a bent or trigonal pyramidal molecule, will have a net polarity.
In the case of Bei2, the molecule has a linear geometry, which means that the iodine atoms are positioned on opposite sides of the beryllium atom. This symmetrical geometry results in no net polarity for the molecule.
Consequences of Bei2 Polarity: Is Bei2 Polar Or Nonpolar
The polarity of Bei2 has significant consequences for its chemical properties, solubility, and reactivity.
Polarity influences Bei2’s solubility in different solvents. Polar solvents, such as water, have a high dielectric constant, which allows them to solvate polar molecules like Bei2. In contrast, nonpolar solvents, such as hexane, have a low dielectric constant and cannot effectively solvate polar molecules.
Is bei2 polar or nonpolar? To find out, you can take a look at unit 33 test a spanish 2 . This test will help you determine the polarity of bei2 and other related terms.
Reactivity with Other Molecules
Polarity also plays a crucial role in Bei2’s reactivity with other molecules. Polar molecules can interact with each other through electrostatic forces, leading to the formation of ion-dipole or dipole-dipole interactions. These interactions can enhance the reactivity of Bei2, making it more likely to participate in chemical reactions.
Applications of Bei2 Polarity
Bei2 polarity has significant implications in various practical applications. Its ability to form polar interactions with other molecules and surfaces makes it a versatile material with diverse uses.
One of the most important applications of Bei2 polarity is in the field of solvation. Bei2 is a polar aprotic solvent, meaning it does not have a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom. This makes it an ideal solvent for dissolving polar and nonpolar compounds.
Bei2’s polarity allows it to solvate both polar and nonpolar molecules by forming dipole-dipole interactions with polar molecules and van der Waals interactions with nonpolar molecules.
Bei2 polarity also plays a crucial role in its use as a catalyst. In many catalytic reactions, Bei2 acts as a Lewis acid, accepting electron pairs from reactants to form intermediate complexes. The polarity of Bei2 allows it to interact with electron-rich centers in reactants, facilitating bond formation and breaking.
In materials science and nanotechnology, Bei2 polarity has potential applications in the synthesis and design of advanced materials. Bei2 can be used as a template for the growth of polar materials, such as metal oxides and semiconductors. The polarity of Bei2 can also be used to control the self-assembly of nanostructures, leading to the development of novel materials with unique properties.
FAQ Overview
What is polarity?
Polarity refers to the uneven distribution of electrons within a molecule, resulting in the formation of positive and negative poles.
How can we determine the polarity of Bei2?
The polarity of Bei2 can be determined by considering its electronegativity and molecular geometry. Electronegativity measures the ability of atoms to attract electrons, while molecular geometry influences the spatial arrangement of electrons.
What are the consequences of Bei2 polarity?
Bei2 polarity affects its solubility, reactivity, and interactions with other molecules. Polar molecules tend to dissolve in polar solvents and react more readily with other polar molecules.